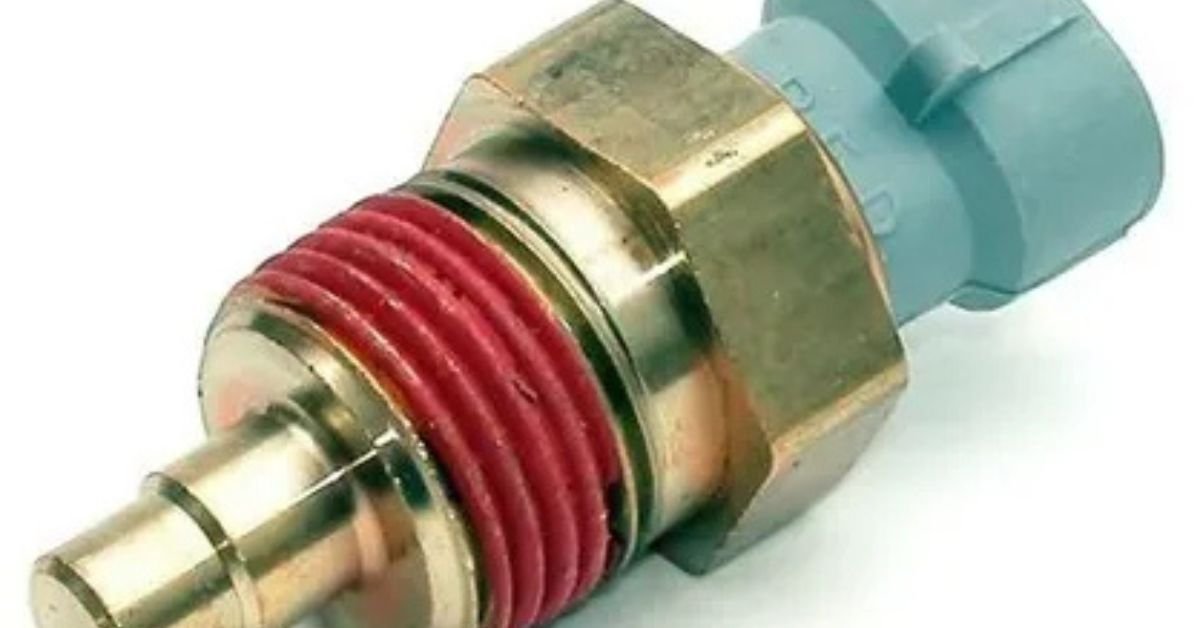
Introduction:
The ECT sensor, or Engine Coolant Temperature sensor, is a small but important part of a car’s engine system.Using this system, the car’s computer is able to measure the coolant temperature.. This helps the engine know when it is cold, warm, or overheating.
Many drivers don’t notice the ECT sensor until a problem happens. If this sensor fails, the engine may run poorly, use more fuel, or show warning lights on the dashboard. This makes the ECT sensor an important part of smooth and safe driving.
In this article, you will learn what the ECT sensor does, how it works, and why it matters for engine performance. We will also briefly discuss common signs of a bad ECT sensor and why timely checks are important.
What Is an ECT Sensor?

An ECT sensor, or Engine Coolant Temperature sensor, is a small device in a car’s engine. It checks the temperature of the engine coolant. This information is sent to the engine control unit to help the engine run properly.
The ECT sensor helps control fuel use, engine timing, and cooling fan operation. If it does not work correctly, the engine may overheat or run rough. That is why this small sensor plays a big role in engine performance.
Definition and Full Form of ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor)
ECT stands for Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor. It is a small sensor that keeps an eye on the engine’s heat level. The sensor measures how hot the engine coolant is and sends this data to the car’s computer. This helps the engine stay within a safe temperature range.
Think of the ECT sensor as the engine’s temperature messenger. It helps the vehicle decide how much fuel to use and when to turn the cooling fan on. Even though it is small, it supports many engine functions, such as:
- Maintaining the correct engine temperature
- Helping the engine start smoothly in cold weather
- Preventing engine overheating
Why It’s Called “ECT Sensor” in Vehicles
It is called an ECT sensor because it measures the engine coolant temperature. The word “engine” refers to the car’s motor. It is the temperature of the coolant that determines how hot or cold it is.
All three words explain exactly what the sensor does. It senses the coolant’s heat and reports it to the vehicle’s computer. That is why the name ECT sensor is simple, clear, and directly linked to its job in the engine system.
How the ECT Sensor Works in Your Engine
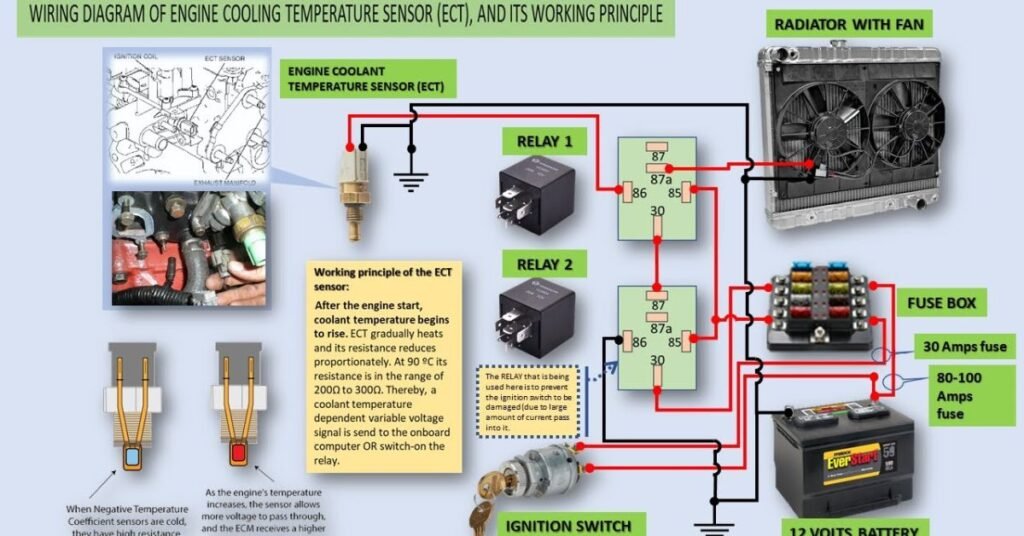
ECT sensors measure the temperature of engine coolant.. It changes its electrical resistance depending on how hot or cold the coolant is. This information is sent to the engine control unit (ECU) to help the engine run efficiently.
The ECU uses this data to make important decisions, such as:
- Adjusting the fuel injection for better performance
- Controlling the cooling fan to prevent overheating
- Helping the engine warm up faster in cold weather
Even though it is small, the ECT sensor plays a key role in keeping your engine safe and running smoothly.
Thermistor Principle: Understanding NTC Sensors
The ECT sensor works on the thermistor principle. Most ECT sensors use an NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistor. This means the sensor’s resistance decreases as the temperature rises. Simply put, hotter coolant → lower resistance; cooler coolant → higher resistance.
NTC sensors are clever and simple, and they help the engine in many ways. Some unique ways they work include:
- Talking in resistance: The sensor “speaks” to the ECU by changing electrical resistance.
- Smart timing: Helps the engine know exactly when to adjust fuel and spark.
- Coolant watchdog: Monitors the coolant constantly to prevent overheating.
- Cold start helper: Signals when extra fuel is needed during engine start.
Even a tiny NTC sensor can control big engine decisions, keeping your car safe and efficient.
How the Sensor Sends Signals to the ECU
The ECT sensor sends information about coolant temperature to the engine control unit (ECU). It does this by changing its electrical resistance. The ECU reads these changes and decides how the engine should respond. Engines run smoothly and safely when this is done.
Some unique ways the sensor communicates with the ECU include:
- Resistance language: The sensor changes resistance instead of using words or sounds.
- Pulse translator: Converts temperature changes into electric signals the ECU can read.
- Instant messenger: Sends real-time updates to help the engine adjust immediately.
- Silent guardian: Works quietly but prevents engine damage without the driver noticing.
- Smart alert system: Alerts the ECU to both cold starts and overheating conditions.
Where Is the ECT Sensor Located?
Finding the ECT sensor is easier than you think. It quietly sits in the engine, doing its job without drawing attention.
The ECT sensor is usually installed near the engine’s thermostat or directly in the coolant passage.The exact position depends on the model of the car.. Here are some unique points about its location:
- Thermostat neighbor: Often placed close to the thermostat for accurate temperature readings.
- Coolant stream monitor: Positioned where it can sense the main flow of coolant.
- Hidden helper: Usually tucked away, safe from heat and moving engine parts.
- Wiring access: Located where the sensor’s wires can easily reach the ECU.
- Quick replacement spot: Installed in a way that makes maintenance simpler when needed.
Common Locations in Modern Cars
- Near the thermostat housing: Measures coolant as it leaves the engine.
- On the engine block: Directly senses engine temperature for accurate readings.
- By the cylinder head: Monitors hot spots in high-performance engines.
- Radiator inlet/outlet: Checks coolant temperature entering or leaving the radiator.
- Coolant hose junctions: Positioned where hoses meet for easy access.
- Engine wiring harness area: Close to ECU connections for reliable signal transfer.
- Near the water pump: Monitor coolant flow and temperature together.
- Under intake manifold: Hidden location in some modern compact engines.
- Along the engine coolant passage: Ensures constant monitoring of circulating coolant.
- Thermostat cover top: Convenient spot for maintenance and replacement.
How Location Affects Replacement Difficulty
A sensor hidden deep in the engine can turn a simple replacement into a tricky task. Its position decides how much engine parts need to be moved or removed for access.
What Does the ECT Sensor Do?
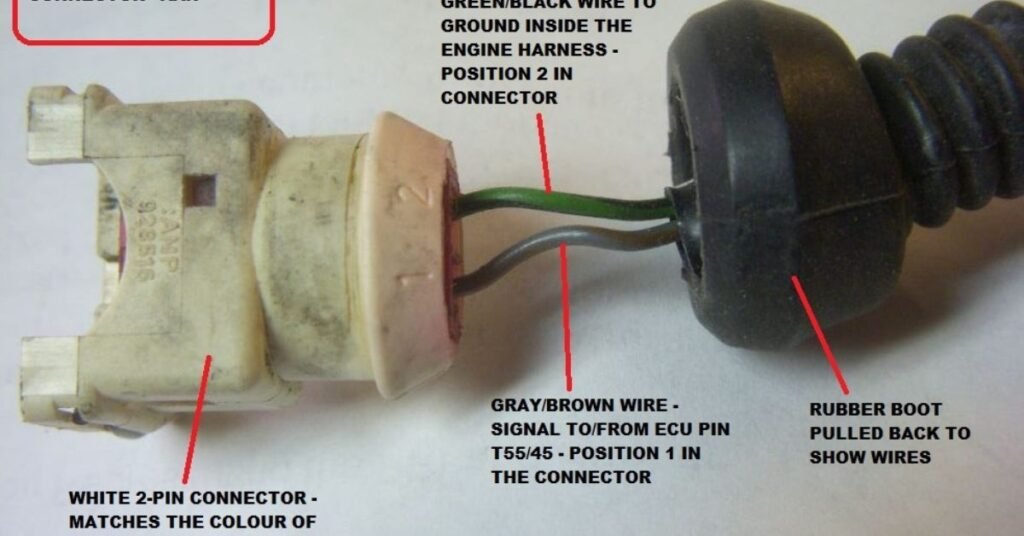
The ECT sensor tells the engine how hot or cold the coolant is. This helps the engine control unit (ECU) make the right decisions for fuel and timing.
It also helps the cooling fan turn on when needed and prevents the engine from overheating. Overall, it keeps the engine running smoothly and efficiently.
Role in Fuel Injection and Ignition Timing
- Fuel fine-tuner: Adjusts the amount of fuel injected based on engine temperature.
- Spark master: Helps decide the exact timing for ignition sparks.
- Cold start booster: Signals for extra fuel when the engine is cold.
- Overheat protector: Reduces fuel flow to prevent engine damage.
- Efficiency enhancer: Balances fuel and spark for smooth performance.
- Emission controller: Helps lower harmful exhaust gases by optimizing combustion.
- Engine response guide: Ensures the engine reacts correctly to temperature changes.
- Adaptive timing aid: Adjusts ignition timing for different driving conditions.
- Fuel saver: Prevents wasted fuel by matching injection to coolant temperature.
- Performance stabilizer: Keeps the engine running steady under load and heat.
Impact on Cooling Fan and Engine Temperature Control
- Fan trigger: Tells the cooling fan when to turn on or off.
- Overheat alarm: Helps prevent the engine from getting too hot.
- Temperature balancer: Keeps the engine running at an optimal heat level.
- Idle cooler: Adjusts fan speed even when the car is not moving.
- Heat flow monitor: Watch how coolant moves through the engine.
- Quick response: Reacts immediately to sudden temperature changes.
- Engine protector: Prevents damage from extreme heat spikes.
- Energy saver: Runs the fan only when needed to save battery power.
- Climate aid: Helps maintain consistent cabin and engine temperature.
- Long-term guardian: Supports engine longevity by controlling heat consistently.
Symptoms of a Bad or Failing ECT Sensor

A failing ECT sensor can cause several engine problems. It may give wrong temperature readings, which confuses the engine control unit.
Common signs of a bad ECT sensor include:
- Check engine light: The dashboard warning may turn on.
- The engine may use more fuel than usual due to poor fuel economy.
- Rough idling: The engine may run unevenly at stops.
- Overheating: Cooling fan may not work properly.
- Hard starting: Engine struggles to start, especially in cold weather.
- Erratic temperature gauge: The gauge may jump or stay fixed.
- Increased emissions: Engines may burn fuel inefficiently.
- Reduced engine performance: The car may feel sluggish or weak.
Poor Fuel Economy and Hard Starts
- Extra fuel in cold starts: ECU thinks the engine is colder than it is.
- Rich fuel mixture: Too much fuel causes smoke or rough running.
- Engine hesitation: The car may stall or struggle to start.
- Longer warm-up time: Engine takes more time to reach the ideal temperature.
- Inconsistent acceleration: The car may jerk or feel weak when accelerating.
- Fuel system stress: Constant over-fueling can wear out engine components.
Check Engine Light and Erratic Temperature Readings
Dashboard warning: Check engine light may turn on unexpectedly.
Jumping temperature gauge: Engine temperature gauge moves up and down quickly.
False overheating alerts: Sensor may signal overheating when engine is fine.
Incorrect coolant reading: ECU gets wrong temperature data.
Intermittent sensor signals: Temperature readings may be inconsistent.
Engine performance issues: Wrong data can affect fuel and ignition timing.
Delayed fan activation: Cooling fan may turn on too late or too early.
Hard to diagnose: Problems may appear randomly, making troubleshooting tricky.
Common ECT Sensor Error Codes
| Error Code | Meaning | Possible Cause | Effect on Engine |
| P0115 | Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty ECT sensor, wiring issue | Engine may overheat or run rich |
| P0116 | Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Range/Performance Problem | Sensor sending incorrect signals | Poor fuel economy, rough idle |
| P0117 | Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Input | Short circuit or damaged sensor | ECU thinks engine is cold, adds extra fuel |
| P0118 | Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Open circuit or disconnected sensor | Overheating warnings, fan may not run |
| P0125 | Insufficient Coolant Temperature for Closed Loop Fuel Control | Faulty sensor or thermostat | Engine runs rich, harder cold starts |
| P0128 | Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature Below Regulating Temp) | Sensor or thermostat issue | Long warm-up time, poor performance |
| P0119 | Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Intermittent | Loose connection or wiring | Erratic temperature readings, check engine light |
| P0120 | Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor and ECT Conflict | Sensor mismatch or wiring issue | Engine may hesitate or stall |
| P0123 | High Input from Temperature Sensor | Sensor damaged | Overheating alerts, fan activation issues |
| P0124 | Low Input from Temperature Sensor | Wiring short or sensor fault | ECU adds extra fuel, poor fuel efficiency |
What Codes Like P0115–P0118 Mean
| Code | Meaning |
| P0115 | Sensor circuit malfunction |
| P0116 | Sensor range/performance problem |
| P0117 | Sensor low voltage signal |
| P0118 | Sensor high voltage signal |
How to Diagnose Sensor-Related Trouble Code
Check the sensor: Look for visible damage or corrosion.
Inspect wiring: Make sure wires and connectors are not loose or broken.
Test resistance: Measure the sensor’s resistance with a multimeter.
Check coolant level: Low or dirty coolant can affect readings.
Monitor live data: Use a scan tool to see real-time temperature signals.
Replace if needed: If the sensor is faulty, swapping it usually fixes the issue
Conclusion
The ECT sensor is a small but very important part of your car. Knowing what an ECT sensor is helps you understand how your engine stays safe and runs efficiently.
A good ECT sensor keeps fuel use normal, prevents overheating, and improves performance. Checking it regularly and fixing problems early can save money and avoid bigger engine issues.
FAQs:
1: Can a Bad ECT Sensor Affect Fuel Economy?
Yes, a faulty ECT sensor can send wrong temperature data, causing the engine to use more fuel than necessary.
2: How Long Do ECT Sensors Typically Last?
ECT sensors usually last 50,000 to 100,000 miles, but lifespan can vary depending on driving conditions and maintenance.
3: What Happens if the ECT Sensor Fails?
A failed sensor can cause rough idling, overheating, hard starts, and poor engine performance.
4: Where Is the ECT Sensor Located?
It is usually near the thermostat, in the engine block, or along the coolant passage.
5: Can I Replace an ECT Sensor Myself?
Yes, if you have basic tools and access to the sensor, it can be replaced easily by following the car manual instructions.

